Click Free Pest Control Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free pest control quote today.
Bat Bugs, Bed Bugs and Relatives by W.S. Cranshaw, M. Camper and F.B. Peairs* (Revised 2/09) Quick Facts... The bed bug (Cimex lectularius) and its relatives (Family: Cimicidae) form a small group of bloodsucking insects. Bat and bed bugs have a short broad head, broadly attached to the prothorax, and an oval body. Because of the different habits of the various bed bugs, proper identification determines where to direct controls to be most effective. Bed bug control is very difficult and requires all infested sites to be effectively treated at the same time.
The bed bug, bat bug and related species of the family Cimicidae, are blood sucking insects that feed on birds and/or mammals. Five of the cimicid bugs are present in Colorado.
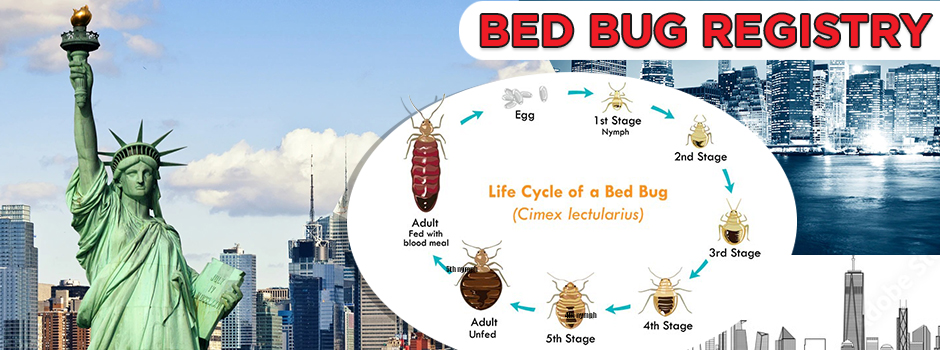
Bed bug (Cimex lectularius). The bed bug is a notorious species and is the only member of this insect family in Colorado that is adapted to living entirely with humans. For several decades following World War II it was largely eradicated form the United States, existing in only small pockets. However, within the past decade it has had tremendous resurgence. Bed bugs can be accidentally carried on furniture, luggage and other materials so problems with bed bugs tend to be most severe in apartments, motels and other sites that see high amounts of human traffic.
Bat bug (Cimex pilosellus). Prior to the recent increase of bed bugs, the bat bug was the most common representative of this group of insects found within homes in Colorado. Bat bugs develop in colonies of roosting bats, which sometimes occur in attics or behind walls of buildings. Bat bugs may move into human living areas and incidentally bite people, with such migrations particularly common when bats migrate or are eliminated from the building. However, in the absence of the bat hosts, these insects cannot sustain and reproduce.
Swallow bug (Oeciacus vicarius). The swallow bug is a parasite of cliff swallows and, less commonly, barn swallows. Problems with human bites occur in homes where swallows attached and maintained nests during the previous summer. Swallow bug bites of humans tend to occur in late winter and spring, when the swallow bugs emerge from winter dormancy in anticipation of the return of their swallow hosts. The insects are largely dormant during the period between the time nests are abandoned in summer and just prior to the return of swallows the following spring.
Poultry bug (Haematosiphon inodorus). Poultry bugs are associated with chickens and other poultry. They hide during the day in cracks and crevices around the poultry roost and move out to feed at night. Human bites are rare and occur when people spend night activities in close proximity to poultry roosting areas.
Hesperocimex coloradensis. Purple martins and, less commonly, woodpeckers and owls are hosts for H. coloradensis. This species is present in the southwestern areas of the state. Encounters with humans occur when bird hosts nest in buildings.
All of these species are generally similar in appearance. They are reddish-brown to grayish-brown with an oval body form and about 3/8-in long when full-grown. All are wingless, although small wing pads are present on the back. Their body is flattened when unfed, although they swell rapidly with a blood meal. The various species found in Colorado can be separated by patterns of hairs, wing pad structures and other features that are summarized in Figure 1.
Bed bugs usually feed in the middle of the night while people sleep and the bite is painless. They often feed for less than 10 minutes before the insect is satiated and returns to a hiding area to digest the meal. A line of bites may appear where several bed bugs have fed along the edge of a sheet or clothing lying next to the skin.
Although the bite is not immediately felt, people often react to the proteins of the bed bug saliva introduced during biting. Typically, a reddish swelling,("wheal")may develop, associated with some swelling and itching. There may be little response immediately following the bite with peak itchiness being noticed at about a week, then gradually declining. Repeated exposure to bed bug bites may produce more intensive reactions and itchiness. However, these reactions are highly variable and some people show little response while others react strongly. Regardless of the symptom that develops, there is nothing unique about bed bug bites that can be used for positive diagnosis. The detected presence of bed bugs is needed to determine if a reddish bite might be from bed bugs.
View post:
Bat Bugs and Bed Bugs
- Papa Juke Doing the New Revised Bed Bug Blues [Last Updated On: September 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 5th, 2011]
- EnviroPest -Boulder Pest Control, Bed Bug Exterminator [Last Updated On: September 7th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 7th, 2011]
- Bed bug in five star hotel ( RACV Royal Pines Resort in Australia )003 [Last Updated On: September 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 8th, 2011]
- Rodney the Colorado Bed Bug Inspection Dog - EnviroPest [Last Updated On: September 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 8th, 2011]
- Doogie the Denver Bed Bug Dog mrbedbugdog [Last Updated On: September 18th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 18th, 2011]
- Bugged Out Pest Control | Salt Lake City Utah | Colorado [Last Updated On: September 21st, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 21st, 2011]
- Macaroni - Bed Bug Dog.wmv [Last Updated On: September 23rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 23rd, 2011]
- Mountain Pest Control Inc [Last Updated On: September 24th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 24th, 2011]
- Red Roof Inn Bed Bug Infestation [Last Updated On: September 28th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 28th, 2011]
- Bed Bugs Specialists [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2011]
- 1000 Bed Bugs Feeding at Once - Video [Last Updated On: October 15th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 15th, 2011]
- Colorado Bed Bug Dog Bugsy - Video [Last Updated On: November 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 8th, 2011]
- Bedbug Treatment video Bedbug Blasters - Video [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2011]
- Colorado Elite Pest Control Westminster - Video [Last Updated On: November 17th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 17th, 2011]
- WARNING - BE VERY AWARE - BED BUGS INCREASING - 1 - Video [Last Updated On: December 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 8th, 2011]
- Bed bug heater - Video [Last Updated On: December 10th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 10th, 2011]
- State Rep. convenes bed bug task force [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2012]
- Railroad project will evict squatters from The Point [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2012]
- What to do if you have bed bugs - Video [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2012]
- What U.S. City Tops List For Bed Bugs? [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2012] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2012]
- Entomologists to discuss insect issues at annual meeting [Last Updated On: May 30th, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 30th, 2012]
- Bed bug infestation tied to GJ property mgmt. company [Last Updated On: June 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 7th, 2012]
- Experts are serious when they say 'don't let the bed bugs bite' [Last Updated On: June 20th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 20th, 2012]
- Bed Bugs Colorado Springs - Video [Last Updated On: October 31st, 2012] [Originally Added On: October 31st, 2012]
- Bed Bug Killer Spray and Treatments from BedBugKiller.co.uk [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Colorado Bed Bug K9 - Cherry Creek - Denver, CO [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Bed Bug Treatment – Control Bugs in London, Sussex, Surrey and Kent [Last Updated On: November 8th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 8th, 2013]
- Bat Bugs and Bed Bugs - Colorado State University [Last Updated On: November 9th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 9th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs - Colorado Pest Management [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2013]
- Bed Bug Treatment – Control Bugs in London, Sussex, Surrey ... [Last Updated On: November 18th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 18th, 2013]
- Bedbug Myths - Bed Bugs Limited [Last Updated On: December 19th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 19th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Prevention and Control [Last Updated On: December 19th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 19th, 2013]
- COLORADO Bed Bugs | Call: 1-800-922-2250 for Pest Control | Home [Last Updated On: December 26th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 26th, 2013]
- Colorado Springs ranks in top 50 cities for bed bugs [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Colorado Springs ranks in top 50 cities for bed bugs : News ... [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Colorado Springs ranks in top 50 cities for bed bugs ... [Last Updated On: January 23rd, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 23rd, 2014]
- COLORADO Bed Bugs | Call: 1-800-922-2250 for Pest Control ... [Last Updated On: January 23rd, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 23rd, 2014]
- Pitt Co. Elementary School Fights Spread Of Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2014] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2014]
- Bed Bugs - Bed Bug Treatment- Thermal Clean [Last Updated On: May 3rd, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 3rd, 2014]
- Spray For Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co Rest Easy Bed Bug Spray - Video [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2014]
- Getting Rid Of Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co How To Avoid Bed Bugs - Video [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2014]
- How To Remove Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co Bed Bugs On Bed - Video [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2014]
- How To Prevent Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co Termite Ntrol San Diego - Video [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2014]
- Home Remedy For Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co Bee Removal Mesa Az - Video [Last Updated On: May 9th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 9th, 2014]
- Rid Of Bed Bugs Colorado Springs Co How To Get Rid Of Bed Bugs Yourself - Video [Last Updated On: May 10th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 10th, 2014]
- Pitt Co. warns of bed bugs - Greenville, NC | News ... [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2014]
- Sleep Tight, LLC - Pest Control Service | Bed Bug Removal ... [Last Updated On: October 15th, 2014] [Originally Added On: October 15th, 2014]
- Six Shandoka Apartments Treated for Bed Bugs : the Watch [Last Updated On: October 31st, 2014] [Originally Added On: October 31st, 2014]
- Thinking About Bed Bugs Treatment in Silverthorne, CO 80498 [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2014] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2014]
- Bed Bugs Stage A Comeback In Colorado [Last Updated On: December 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: December 8th, 2014]
- Bed bug warriors gather in Denver summit [Last Updated On: January 10th, 2015] [Originally Added On: January 10th, 2015]
- Ouch! Denver ranks eighth among U.S. cities for bed bugs [Last Updated On: January 21st, 2015] [Originally Added On: January 21st, 2015]
- These Are the Cities With the Most Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2015] [Originally Added On: January 29th, 2015]
- Bed bug infestation - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia [Last Updated On: February 6th, 2015] [Originally Added On: February 6th, 2015]
- Bed Bugs Appearance and Life Cycle | Bed Bugs: Get Them ... [Last Updated On: September 24th, 2015] [Originally Added On: September 24th, 2015]
- Bed Bug Relief - How To Treat Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 13th, 2015] [Originally Added On: October 13th, 2015]
- Bed Bugs - Colorado State University Extension [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Bugs that Look Like Bed Bugs | bed-bugs.com [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs - Jefferson County, Colorado [Last Updated On: May 1st, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 1st, 2016]
- Bed Bugs - Boulder County, Colorado [Last Updated On: May 5th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 5th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs & Traveling Tips | Mug a Bug Pest Control ... [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2016]
- Bat Bugs, Bed Bugs and Relatives - 5.574 - Colorado State ... [Last Updated On: May 8th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2016]
- The Best Bed Bug Exterminator Denver Colorado Has to Offer ... [Last Updated On: May 20th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 20th, 2016]
- Bed bug bites and bed bugs: how to tell if you have them [Last Updated On: December 25th, 2016] [Originally Added On: December 25th, 2016]
- How not to spread bed bugs when you travel - Bedbugger.com [Last Updated On: December 29th, 2016] [Originally Added On: December 29th, 2016]
- Colorado Tri-Flo Signs Distribution Agreement with Bed Bug Supply - PCT Magazine [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2017] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2017]
- Campus resources for bed bug detection - CU Boulder Today [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2017] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2017]
- Disgruntled man releases bedbugs in Maine city office - Colorado Springs Gazette [Last Updated On: June 5th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 5th, 2017]
- Bed Bugs Colorado [Last Updated On: June 16th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 16th, 2017]
- TARGET 13: Bed bug fiasco at Extended Stay America in Colorado Springs - KRDO [Last Updated On: July 18th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2017]
- No regulations for bed bugs...why not? - KRDO [Last Updated On: July 18th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2017]
- Bedbugs turn stay at Colorado Springs hotel into a nightmare - The Denver Post [Last Updated On: July 18th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2017]
- Bed bug infestation sweeping metro Denver - FOX31 Denver [Last Updated On: July 20th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 20th, 2017]
- Apartment bedbug infestation persists after treatments - FOX31 Denver [Last Updated On: August 1st, 2017] [Originally Added On: August 1st, 2017]
- Aurora man says new mattress was delivered with bed bugs - The Denver Channel [Last Updated On: August 13th, 2017] [Originally Added On: August 13th, 2017]
- Bed Bug Infestations Earn DC National Ranking - Patch.com [Last Updated On: August 27th, 2017] [Originally Added On: August 27th, 2017]
- Bed Bugs | Pueblo County, Colorado [Last Updated On: May 19th, 2018] [Originally Added On: May 19th, 2018]
- Difference between Ticks and Bed bugs | Ticks vs Bed bugs [Last Updated On: May 20th, 2018] [Originally Added On: May 20th, 2018]
- The Absolute Best Bed Bug Treatment - Heat Pro Bed Bug Removal [Last Updated On: June 6th, 2018] [Originally Added On: June 6th, 2018]
- How to Eliminate Bed Bugs - PF Harris [Last Updated On: August 17th, 2018] [Originally Added On: August 17th, 2018]
Click Free Exterminator Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free exterminator quote today.