Bed bugs are not a health hazard but they can create a lot of stress. Learn how you can protect yourself and help stop the spread of bed bugs.
Bed bugs are small, brown insects - about the size of an apple seed at adult stage - that feed on human blood. After a feeding, they swell in size and can become bright or dark red. They are wingless and cannot fly or jump. They hide during the day and come out at night in areas where people sleep.
There is no evidence bed bugs spread diseases to humans. Reactions to bites range from no reaction at all, to itchy red bumps. If a bed bug is disturbed during feeding, they may bite more than once in the same general area. The bites are painless but may become itchy after a day or two. Scratching at the bites may cause an infection. Many people get anxious and distressed when exposed to bed bugs.
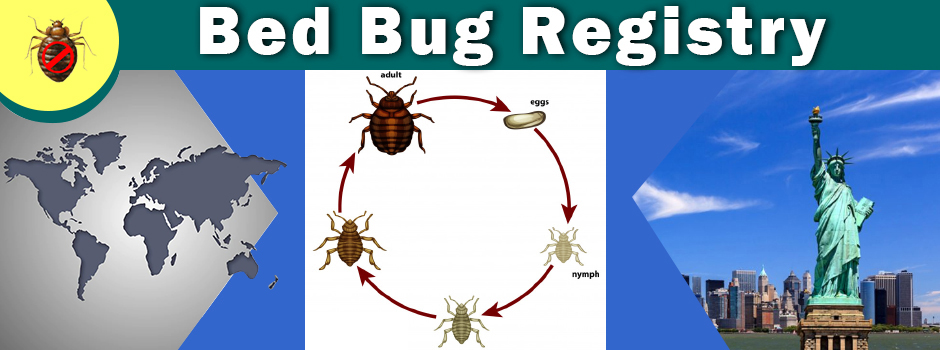
There are three stages in the life of a bed bug: eggs, nymphs(or juveniles) and adults. The eggs have a coating that helps them stick to objects and they usually hatch in six to 17 days. Hatched nymphs start to feed right away. Adult bed bugs can live for more than 12 months, depending on the location or conditions and can become inactive when there is no host to feed on.
Having bed bugs does not mean your home isn't clean. They enter your home on items you carry in from outside. The most common items are mattresses, box springs, upholstered furniture, luggage, electronics, books, pictures and household goods. A sign you have bed bugs is finding (on your mattress, box spring, pillow, etc):
If there is a lot of bed bugs, a musty or sweet odour, like coriander, may be present.
The best way to deal with bed bugs is to avoid bringing them into your home.
When you return home:
More here:
Province of Manitoba | What You Should Know About Bed Bugs
- Little Bugs = Big Trouble [Last Updated On: September 7th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 7th, 2011]
- Hundreds of Bed Bugs Biting a Man's Arm - Video [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2012] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2012]
- MOBILE BED BUG TREATMENT | Green Heat Purification - Bed Bugs Heat ... [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Winnipeg Information - City of Winnipeg - Official City ... [Last Updated On: November 9th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 9th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Winnipeg Information [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2013]
- The Bed Bug Resource » Heat Treatment [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2013]
- MOBILE BED BUG TREATMENT | Green Heat Purification - Bed Bugs ... [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2013]
- New Label for Bedbugs Proposed | Canada Bedbugs [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Winnipeg Resources and Treatment Tips [Last Updated On: November 30th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 30th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Winnipeg | Energy Retrofit Winnipeg | Manitoba Green ... [Last Updated On: December 12th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 12th, 2013]
- Manitoba Declares War on Bedbugs | Canada Bedbugs [Last Updated On: December 25th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 25th, 2013]
- bed bugs - The Manitoba Teachers' Society [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2014]
- Bed bugs: dos and donts Got bed bugs? Bedbugger.com [Last Updated On: June 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: June 2nd, 2014]
- BED BUGS - Review of Victoria Inn, Winnipeg, Manitoba ... [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2015] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2015]
- "Dragnet" to kill bed bugs. PEST CONTROL CANADA [Last Updated On: June 18th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 18th, 2017]
- Health cares reaction to bed-bug epidemic likened to ... [Last Updated On: October 6th, 2017] [Originally Added On: October 6th, 2017]
- How To Kill Bed Bugs With Heat | Heat Assault | Heat Assault [Last Updated On: October 17th, 2017] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2017]
- Saskatoon Bed Bug Control & Bud Bug Heat Treatment ... [Last Updated On: January 30th, 2018] [Originally Added On: January 30th, 2018]
- Manitoba, Canada Bed Bug Registry Map Bed Bug Infestation Reports and Google ... [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2018] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2018]
- Manitoba housing IPMG Got Bed Bugs? Bedbugger Forums [Last Updated On: September 7th, 2018] [Originally Added On: September 7th, 2018]
- Montreal Immigration and Refugee Board forced to close down due to bed bug infestation - The Post Millennial [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2019] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2019]