What is a bed bug?
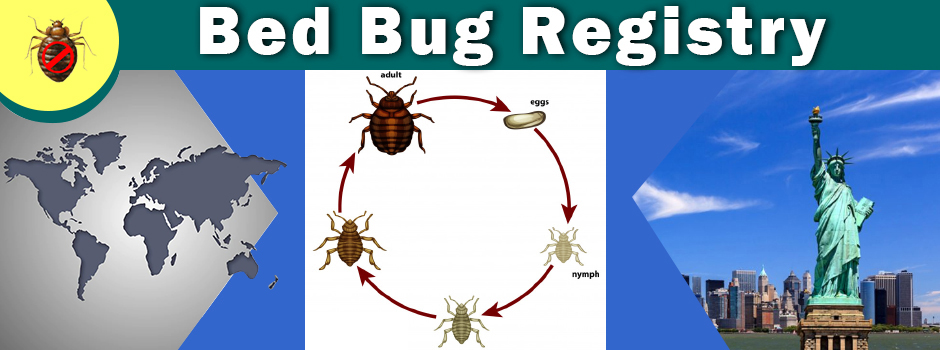
Bed bugs are small, reddish-brown insects with flat, oval bodies. They are usually 5 to 7 millimetres long (3/8 of an inch). They cannot fly, but can travel quickly. Bed bug nymphs (babies) are about 1 to 4 millimetres long and yellow-white in colour.
Bed bugs feed on the blood of humans and animals. Unlike some parasites, such as fleas or lice, bed bugs do not live on their hosts, but only visit them to feed. They are most active at night and usually feed weekly. Most live for 4 to 6 months, but some may live up to a year with no food. Female bed bugs can lay about 500 eggs in their lifetime.
A bed bug bite usually causes a red bump or flat welt that may be itchy. Bed bugs tend to bite exposed parts of the body (not covered by clothes) such as the face, neck, arms and hands. Several bites may occur close together on the body because bed bugs usually feed more than once. The bites take 1 to 2 weeks to go away.
Bed bugs prefer to hide close to their hosts, which is why their first choice is beds. They can be found in homes, hotels, student residences and shelters. Bed bugs can hitch a ride on such things as clothing, backpacks, luggage and even books.
There is no evidence that bed bugs spread disease to people. However, public health officials remain concerned about bed bugs because scratching a bite can sometimes cause a skin infection, which can become serious. Applying an antiseptic lotion or antibiotic cream to the area can help prevent infection.
Bed bug infestations can cause significant stress, worry, and insomnia (not being able to sleep). In addition, getting rid of bed bugs can be expensive and time consuming.
Symptoms of an infection include:
If you have symptoms, contact your health care provider or call 8-1-1 to speak to a registered nurse.
Some people may have an allergic reaction to a bed bug bite, usually a small skin reaction in the bite area. In rare cases, some may have severe reactions. Allergic sensitivity may increase the more a person is bitten. If you are concerned about your symptoms, see your health care provider.
Bite marks on your body, especially around your face, neck, arms and hands, are a sign of bed bugs. To know for sure that you have bed bugs look for the following signs:
You should inspect the following areas for bed bugs:
Try to collect a bed bug for identification. Contact a pest control professional or your local health authority if you need help.
To stop bed bugs from entering your home:
There are nonchemical and chemical options for treating bed bug infestations. Often, both types of treatments will be required. Getting help from a qualified pest management professional is recommended. Pest control companies often use chemical insecticides or very high heat. More than one application will likely be necessary.
Building owners should check municipal bylaws before trying to treat infestations on their own.
For more information on how to get rid of bed bugs or to find a licensed pest control company in your areas, visit:
Read the original post:
Bed Bugs | HealthLinkBC File 95
- Bed Bug Inspection Dog in Ontario, Canada [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2011]
- Tracker The Bed Bug Dog In Action [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2011] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2011]
- Fighting Bed Bugs in Canada with ThermaPure CTV News - August 2010 [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2011]
- Treating a bed frame for bedbugs using Diatomaceous Powder [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2011]
- When the bed bug bites-One Woman's Story [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2011] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2011]
- "Mel, Niagara, Tongue and Bed Bugs" Mattoliver's photos around Toronto, Canada [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2011] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2011]
- Bed Bug gets owned [Last Updated On: May 20th, 2011] [Originally Added On: May 20th, 2011]
- The Bed Bug Epidemic [Last Updated On: May 24th, 2011] [Originally Added On: May 24th, 2011]
- Bed Bug Heat Treatment [Last Updated On: May 30th, 2011] [Originally Added On: May 30th, 2011]
- Bed bugs invading Winnipeg in public places [Last Updated On: May 31st, 2011] [Originally Added On: May 31st, 2011]
- Tracker The Bed Bug Dog on Breakfast Television [Last Updated On: June 3rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 3rd, 2011]
- Why ThermaPureHeat is the #1 most effective way to kill bed bugs and their eggs. [Last Updated On: June 9th, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 9th, 2011]
- Hospital Turns Patient Away Due to Bed Bug Bites [ABC: 5-28-2011] [Last Updated On: June 10th, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 10th, 2011]
- Bed Bugs 8.1 Kanas Earthquake Dream Mega Tornado Sickness Earthquakes. and More [Last Updated On: June 12th, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 12th, 2011]
- Bed bug thermal heat treatment | How to get rid of Bed bugs using heat thermal remediation.mov [Last Updated On: June 22nd, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 22nd, 2011]
- Where do Bed Bugs live and How to Get Rid of Them [Last Updated On: June 23rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 23rd, 2011]
- How To Stop Bedbugs [Last Updated On: June 24th, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 24th, 2011]
- Bed Bugs in the NWT [Last Updated On: June 25th, 2011] [Originally Added On: June 25th, 2011]
- Chase our Bed Bug Dog training [Last Updated On: July 15th, 2011] [Originally Added On: July 15th, 2011]
- Latex Mattresses for NYC, LA, Houston, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Philadelphia and more! [Last Updated On: July 20th, 2011] [Originally Added On: July 20th, 2011]
- Cryonite Science Behind Freezing.mp4 [Last Updated On: July 28th, 2011] [Originally Added On: July 28th, 2011]
- Research shows bedbugs can carry superbug MRSA [Last Updated On: August 11th, 2011] [Originally Added On: August 11th, 2011]
- 128. Don't Let The Bedbugs Bite! [Last Updated On: September 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 4th, 2011]
- Bed Bug Awareness [Last Updated On: September 10th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 10th, 2011]
- Bedbug Lillie 4 Chatham, Ontario [Last Updated On: September 30th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 30th, 2011]
- Bed bug inspection Hollywood, Bed Bug exterminator Koreatown, exterminator koreatown, 213-928-7721 [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2011]
- LA Pest Control - Mice, Roach, Rat, Bed Bug Removal 213-928-7849 [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2011]
- Treating a Baseboard with DE to Prevent Bedbugs [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2011]
- Bedbugs Prevention - Reduce Your Clutter! [Last Updated On: October 10th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 10th, 2011]
- HOW TO STOP BEDBUGS CLIMBING INTO YOUR BED - Video [Last Updated On: October 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2011]
- VTS_01_1.VOB - Video [Last Updated On: October 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2011]
- BEDBUGS AND BEDTIME - STOP THE AFFAIR - Video [Last Updated On: October 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2011]
- BED BUGS, PUNAISES DE LITS - Video [Last Updated On: October 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2011]
- BEDBUGS - BED BUGS - Cimex lectularius - Video [Last Updated On: October 16th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2011]
- Bed Bug Thermal Treatment Private Home by A3 Superior Pest Control - Video [Last Updated On: October 17th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2011]
- BED BUG DOG - Inspections - Video [Last Updated On: October 17th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2011]
- Bedbugs - Video [Last Updated On: October 21st, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2011]
- bed bug : improvise mortar and pestle to crush silica gel cat litter, food, makeup - Video [Last Updated On: October 22nd, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 22nd, 2011]
- Bed bug inspection 213-928-7721, santa monica, west side, Bed bug exterminator - Video [Last Updated On: October 24th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2011]
- Bed Bugs - Key Facts and Information - Orkin PCO Canada - Video [Last Updated On: October 26th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 26th, 2011]
- How to do a bed bug room inspection - Orkin PCO Canada - Video [Last Updated On: October 26th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 26th, 2011]
- bed bug exterminator Pasadea - CALL 213-928-7721 bedbugs, roaches + more - Video [Last Updated On: October 26th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 26th, 2011]
- fruit fly trap difficult problem simple solution comedy bedbug bed bug powder SNL bulldog lipstick - Video [Last Updated On: October 29th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 29th, 2011]
- Treating a Cable Outlet to Prevent Bedbugs - Video [Last Updated On: November 23rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2011]
- BATCH of bed bugs and PUBES on my face! - Video [Last Updated On: November 23rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2011]
- WHERE BEDBUGS COME FROM - PLUG IN - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2011]
- HOW TO KEEP BEDBUGS AWAY FROM YOUR HOME - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2011]
- HOW TO STOP BEDBUGS COMING THRU YOUR WALLS - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2011]
- All About Bed Bugs with "At Home" - Video [Last Updated On: November 26th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 26th, 2011]
- Prevent Bedbugs by Applying Diatomaceous Powder - Video [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2011]
- Bed bugs Part 2: Identifying and inspecting for bed bugs - Video [Last Updated On: December 7th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 7th, 2011]
- Vancouver bed bug heat treatment - Video [Last Updated On: December 9th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 9th, 2011]
- bed bugs inspections long beach 213-9287721, rossmoor, seal beach, lakewood - Video [Last Updated On: December 12th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 12th, 2011]
- EucoClean 3in1 vs Bed Bugs Laboratory Test (Every Hotel in the World take note!) - Video [Last Updated On: December 14th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 14th, 2011]
- When Bedbugs Attack! - Video [Last Updated On: December 15th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 15th, 2011]
- Don't matter - it proves evolution. This is Genesis Week, Season 1, Episode 1 - Video [Last Updated On: January 6th, 2012] [Originally Added On: January 6th, 2012]
- Toronto woman recounts vacation nightmare in Cuba [Last Updated On: February 2nd, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 2nd, 2012]
- Iqaluit bed bug problem began months ago, says government [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2012]
- bed bug exterminator, westchester, LAX - CALL 213-928-7721 bedbugs, roaches, ants - Video [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2012]
- Craig Ferguson 10/6/11E Late Late Show Dan Riskin - Video [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2012]
- MEGA Babies "Don't let the Bed Bugs Bite" Pt 1 of 2 - Video [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2012]
- Toronto council debates OMB, affordable housing funding & other issues [Last Updated On: February 8th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 8th, 2012]
- Bed Bug Proof Laundry Bag - www.CorporateTravelSafety.com. - Video [Last Updated On: February 8th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 8th, 2012]
- Live: 2012 Academy Awards [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2012]
- The 2012 Academy Awards [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2012]
- And the winners are ... [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2012]
- 2012 Academy Awards [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2012]
- All Oscars accounted for [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2012]
- Top Entomologists Call 2012 Pivotal Year in Bed Bug War [Last Updated On: February 29th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 29th, 2012]
- According to Rest Assured MC, Freezing Bed Bugs with Cryonite will Become One of the Most Popular Methods for Killing ... [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2012] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2012]
- Allergy Technologies Signs Exclusive Agreement with Hospi-Tel to Distribute ActiveGuard™ Mattress Liners to the ... [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2012] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2012]
- Nodding approval for a new mattress [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 4th, 2012]
- New Dundee entrepreneurs tackle bed bug problem [Last Updated On: May 30th, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 30th, 2012]
- Entomologists to discuss insect issues at annual meeting [Last Updated On: May 31st, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 31st, 2012]
- Here's Why Renting Your Home Through Airbnb Could Be Illegal [Last Updated On: June 7th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 7th, 2012]
- Bed bugs attack jurors [Last Updated On: June 10th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 10th, 2012]
- Huntsville, Ala., offers look at rocket science, history, gardens and more [Last Updated On: June 17th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 17th, 2012]
- Spring Air Partners with Protect-A-Bed to Redefine the Sleeping Experience [Last Updated On: June 28th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2012]
- Organic Plant Health, Inc., (OTCQB: OPHI), Introduces New and Improved Eco-Cedar™ All-Natural Bed Bug Killer. [Last Updated On: July 6th, 2012] [Originally Added On: July 6th, 2012]
- Bedbug-detection dog sniffs out critters at Central Library [Last Updated On: July 20th, 2012] [Originally Added On: July 20th, 2012]