Click Free Pest Control Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free pest control quote today.
IDENTIFICATION AND BIOLOGY
Bedbugs are pests of humans, domestic animals, bats, rodents, rabbitsand wild birds. Worldwide,two species commonly attack humans. One of these, Cimex lectularius, is widely distributed over most of the world, and it is the species that is most common in temperate North America.
During the first half of the 20th century, the bed bug was a common household pest and was a scourge for travelers, for it was common even in respectable hotels. The importance of this insect gradually diminished with improvements in household cleanliness, personal hygiene and the increased availability and use of effective residual insecticides. In developed nations, they declined in incidence, and infestations became a rare event. In the last few years, this downward trend has started to reverse, and globally there have been reports of an increase in bed bug numbers.
Bed bugs are wingless insects, roughly oval in shape, 5-6 mm long when fully grown and fast crawlers. The juvenile stagesare pale cream colored, and the adults are rust brown,becoming adeeper red-brown following a blood meal. Bed bugs are dorsoventrally (top to bottom)flattened and can hide in cracks and crevices, making detection very difficult.
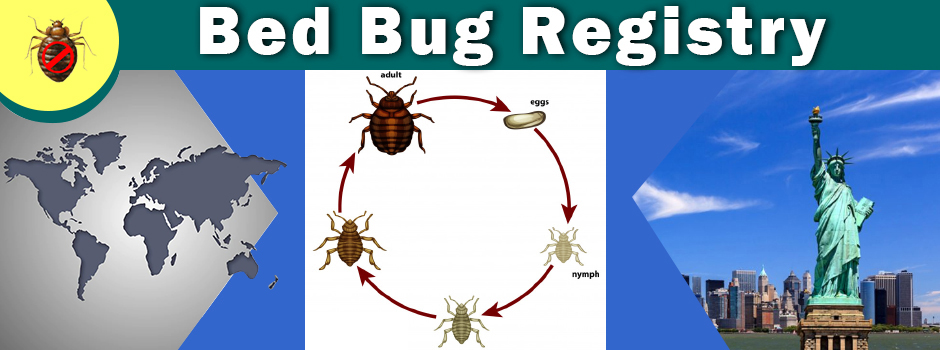
There are five juvenile stages known as nymphs, each lasting 2.5 to 10 days. The nymphs are miniature versions of the adults in general appearance. Each nymphal stage requires at least one blood meal to molt to the next stage, and it takes 3-5 minutes to complete a blood meal. The length of the lifecycle is extremely variable and is dependent on temperature. The temperature threshold for development is about 60 degrees, with optimal development at 86 degrees. The total development time from egg to adult for C. lectularius varies from 24 days at 86degrees to 128 days at 65 degrees. In average conditions, around 74 degrees, the lifecycle takes around two months to complete.
All nymphal stages and adults of both sexes require blood for nutrition and development. At low temperatures, nymphs may survive for five to six months without feeding, whereas adults can survive even longer. For example, in cold conditions, they can live almost two years, even without a blood meal. Mated females usually feed to engorgement and then begin to lay eggs three to six days later. Typically, each female lays two to three eggs a day. The cream-colored eggs are cemented on rough surfaces of hiding places, and nymphs will hatch within approximately nine days at a room temperature of 74 degrees. Also, depending on environmental conditions, female bed bugs may feed every three to four days.
The mouthparts of bedbugs are especially adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. Bed bugs respond to the body warmth of a host and quickly locate a suitable feeding site. They tend not to live on humans, and the only contact is for a blood meal. Blood feeding typically occurs at night.They tend to seek shelter during the day and are inactive while digesting the blood meal. However, bed bugs are opportunistic and will bite in the day, especially if starved for some time.
Bed bugs seek shelter in a variety of dark locations, mostly close to where people sleep. These include under mattresses, floorboards, paintings andcarpets; in various cracks and crevices of walls; within bed frames and other furniture; and behind loose wallpaper. Bed bugs typically stay in close contact with each other, and heavy infestations are accompanied by a distinctive sweet, sickly smell. Blood spotting on mattresses, bed linen, nearby furnishings and walls is often a telltale sign of an infestation.
Bed bugs are public health pests largely because of their nuisance biting, and often the most serious health aspect for many individuals is the mental trauma of knowing there is an infestation. Skin reactions, which are commonly associated with bed bugs, result from the saliva injected during feeding. Some people do not react to their bite, whereas others can experience a great deal of discomfort and loss of sleep from the persistent biting. The most commonly affected areas of the body are the arms and shoulders. Reactions to the bites may be delayed, with up to nine days before lesions appear. Common allergic reactions include the development of large wheals, which are accompanied by itching and inflammation. The wheals usually subside to red spots and can last for several days.
Although it hasbeen suggested that bed bugs may transmit of a wide variety of infectious agents, there has never been a proven case of a disease agent being passed on to humans by bed bugs.
Original post:
Bed Bugs - LSU AgCenter
- Salvant Environmental Services [Last Updated On: September 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 5th, 2011]
- Bed Bug Dog Henry finds living bedbugs in New Orleans [Last Updated On: September 11th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 11th, 2011]
- Mark Knopfler - Cannibals + lyrics [Last Updated On: September 21st, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 21st, 2011]
- Swamp Boat Tour - Spanish Moss [Last Updated On: September 25th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 25th, 2011]
- Bed Bugs Found In Apartment Complex [Last Updated On: October 2nd, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 2nd, 2011]
- Louisiana's Amazing Bed Bug Dogs put to the test [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2011]
- Dogs Hunt Bed Bugs - Video [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2012] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2012]
- Cannibals - Lyrics and Chords - La terre avant le deluge Illustrations Spin - Video [Last Updated On: January 20th, 2012] [Originally Added On: January 20th, 2012]
- Bed Bug Registry Database Louisiana, Usa, National Bed Bug ... [Last Updated On: November 6th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 6th, 2013]
- Bed Bug Sniffing Dogs [Last Updated On: December 23rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 23rd, 2013]
- Bed Bugs Handbook on How to Get Rid of Bedbugs [Last Updated On: December 23rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 23rd, 2013]
- Types of Bedbugs - Bed Bug Types, List of Bedbug Species [Last Updated On: January 10th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 10th, 2014]
- Louisiana bed bug law - Apartments | PRLog [Last Updated On: January 31st, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2014]
- Bed Bugs - Arrow Pest Control Baton Rouge Louisiana [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2014]
- Bed Bugs Rank Most Feared in Apartment Renter Survey - PR ... [Last Updated On: October 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: October 2nd, 2014]
- KCK assisted living facility battling bed bugs - KPLC 7 ... [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2014] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2014]
- KCK assisted living facility battling bed bugs - WAFB 9 ... [Last Updated On: November 20th, 2014] [Originally Added On: November 20th, 2014]
- How To Get Rid of Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: August 13th, 2015] [Originally Added On: August 13th, 2015]
- Bed Bugs - Cornell University [Last Updated On: August 30th, 2015] [Originally Added On: August 30th, 2015]
- FAQ: Is there an insect that will eat bed bugs ... [Last Updated On: September 24th, 2015] [Originally Added On: September 24th, 2015]
- Bed Bugs - Arrow Termite and Pest Control [Last Updated On: October 30th, 2015] [Originally Added On: October 30th, 2015]
- Louisiana & Mississippi Bed Bugs Control - Fischer ... [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- How To Get Rid of Bed Bugs Lafayette, Louisiana - Pest Control [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Northwest Houston hotel guest bitten by bed bugs - KPRC [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2016]
- Info Center: Learn about Bed Bugs | Terminix [Last Updated On: May 16th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 16th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs Pages | PestMall Blog [Last Updated On: May 22nd, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 22nd, 2016]
- Are These Bed Bugs or Scabies? | Terminix [Last Updated On: July 22nd, 2016] [Originally Added On: July 22nd, 2016]
- Bed Bug Control - Budget Pest Control - Pittsburgh, PA [Last Updated On: June 5th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 5th, 2017]
- Bed Bugs | Louisiana Bed Bug Inspection [Last Updated On: June 23rd, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 23rd, 2017]
- Louisiana, United States Bed Bug Registry Map Bed Bug ... [Last Updated On: November 23rd, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2017]
- Sky Harbor dealing with bed bug issue at Terminal 4 ... [Last Updated On: November 30th, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 30th, 2017]
- Where Does Louisiana Rank on the Worst Bed Bugs List? [Last Updated On: September 17th, 2018] [Originally Added On: September 17th, 2018]
- Bed Bug Lawyer Louisiana Bed Bug Bite Injury Attorney [Last Updated On: January 31st, 2019] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2019]
- Louisiana Bed Bug Hotel and Apartment Reports ... [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2020]
- Bed Bug Cases Downtown LA Law Group [Last Updated On: December 17th, 2020] [Originally Added On: December 17th, 2020]
Click Free Exterminator Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free exterminator quote today.