by Michael F. Potter, Extension Entomologist
University of Kentucky College of Agriculture
Most householders of this generation have never seen a bed bug. Until recently, they also were a rarity among pest control professionals. Bed bug infestations were common in the United States before World War II. But with improvements in hygiene, and especially the widespread use of DDT during the 1940s and '50s, the bugs all but vanished. The pests remained prevalent, though, in other regions of the world including Asia, Africa, Central/South America and Europe. In recent years, bed bugs have also made a comeback in the U.S. They are increasingly being encountered in homes, apartments, hotels, motels, dormitories, shelters and modes of transport. International travel and immigration have undoubtedly contributed to the resurgence of bed bugs in this country. Changes in modern pest control practice - and less effective bed bug pesticides - are other factors suspected for the recurrence.
Bed bugs are mentioned, for example, in medieval European texts and in classical Greek writings back to the time of Aristotle. Other bed bug species prefer to feed on wild hosts, especially bats and birds.
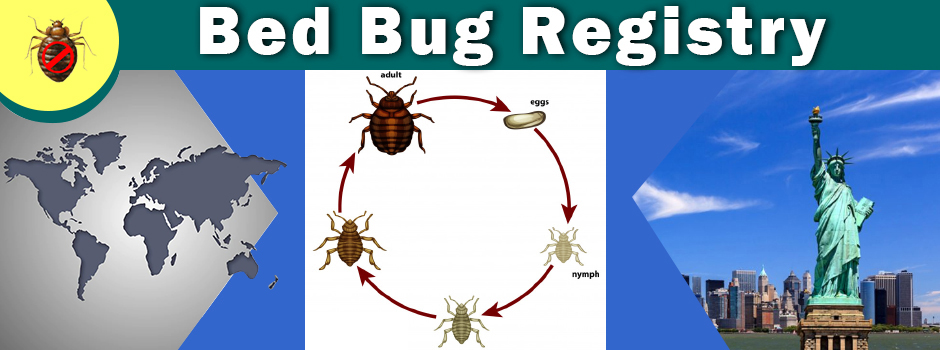
Adult bed bugs are about 1/4 inch long and reddish brown, with oval, flattened bodies. They are sometimes mistaken for ticks or cockroaches. The immatures (nymphs) resemble the adults, but are smaller and somewhat lighter in color. Bed bugs do not fly, but can move quickly over floors, walls, ceilings and other surfaces. Female bed bugs lay their eggs in secluded areas, depositing up to five a day and 500 during a lifetime. The eggs are tiny, whitish, and hard to see without magnification (individual eggs are about the size of a dust spec). When first laid, the eggs are sticky, causing them to adhere to substrates. Newly hatched nymphs are no bigger than a pinhead. As they grow, they molt (shed their skin) five times before reaching maturity. A blood meal is needed between each successive molt. Under favorable conditions (70 - 90 F), the bugs can complete development in as little as a month, producing three or more generations per year. Cool temperatures or limited access to a blood meal extends the development time. Bed bugs are very resilient. Nymphs can survive months without feeding and the adults for more than a year. Infestations therefore are unlikely to diminish by leaving premises unoccupied. Although C. lectularius prefers feeding on humans, it will also bite other warm-blooded animals, including pets.
Bed bugs are active mainly at night. During the daytime, they prefer to hide close to where people sleep. Their flattened bodies enable them to fit into tiny crevices - especially those associated with mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and headboards. Bed bugs do not have nests like ants or bees, but do tend to congregate in habitual hiding places.
Another likely sign of bed bugs is rusty or reddish spots of blood on bed sheets, mattresses, or walls. Heavy infestations may have a musty or "buggy" smell, but the odor is seldom apparent and should not be relied upon for detection.
Bed bugs prefer to hide close to where they feed. However if necessary, they will crawl several feet to obtain a blood meal. Initial infestations tend to be around beds, but the bugs eventually may become scattered throughout a room, occupying any crevice or protected location. They also can spread to adjacent rooms or apartments.
Bed bugs usually bite people at night while they are sleeping. They feed by piercing the skin with an elongated beak through which they withdraw blood. Engorgement takes about three to 10 minutes, yet the person seldom knows they are being bitten. Symptoms thereafter vary with the individual. Many people develop an itchy red welt or localized swelling, which sometimes appears a day or so after the bite. Others have little or no reaction. Unlike fleabites, which occur mainly around the ankles, bed bugs feed on any bare skin exposed while sleeping (face, neck, shoulders, arms, hands, etc.). The welts and itching are often attributed to other causes such as mosquitoes. For these reasons, infestations may go a long time unnoticed, and can become quite large before being detected. The possibility of bed bugs increases if the affected individual has been traveling, or had acquired used beds or furnishings before symptoms started to appear. Bed bugs also are suspect if you wake up with itchy bites you did not have when you went to sleep. Conversely, it is important to recognize that not all bites or bite-like reactions are due to bed bugs. Confirmation requires finding and identifying the bugs themselves, which often requires the help of a professional. (Other possible sources of irritation are discussed in University of Kentucky entomology fact sheet ENT-58: Invisible Itches: Insect and Non-Insect Causes).
A common concern with bed bugs is whether they transmit diseases. Although bed bugs can harbor pathogens in their bodies, transmission to humans is highly unlikely. For this reason, they are not considered a serious disease threat. Their medical significance is mainly limited to the itching and inflammation from their bites. Antihistamines and corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce allergic reactions, and antiseptic or antibiotic ointments to prevent infection. Infestations also may cause anxiety, embarrassment, and loss of sleep.
It often seems that bed bugs arise from nowhere. The bugs are efficient hitchhikers and are usually transported in on luggage, clothing, beds, furniture, etc. Outbreaks can often be traced to travel, especially in countries or cities where bed bugs are common. This is a particular problem for hotels, motels, and apartments, where turnover of occupants is constant. Bed bugs are small, cryptic and agile, escaping detection after crawling into suitcases, boxes, and belongings. The eggs are almost impossible to see when laid on most surfaces. Use of secondhand beds, couches, and furniture is another way that the bugs are transported into previously non-infested dwellings.
Pristine homes, hotels, and apartments have plenty of hiding places and an abundance of warm-blooded hosts. Thus, they are almost as vulnerable to infestation as are places of squalor.
When bed bug-like insects are found, it's important to consider whether bats, swallows, chimney swifts, pigeons, or other wild hosts are involved. Although similar in appearance, bed bug species that normally feed on bats and birds can be differentiated from those that prefer humans. Entomologists and knowledgeable pest control firms can make this determination.
Bed bugs are challenging pests to control. They hide in many tiny places, so inspections and treatments must be very thorough. In most cases, it will be prudent to enlist the services of a professional pest control firm. Experienced companies know where to look for bed bugs, and have an assortment of management tools at their disposal. Owners and occupants will need to assist the professional in important ways. Affording access for inspection and treatment is essential, and excess clutter should be removed. In some cases, infested mattresses and box springs will need to be discarded. Since bed bugs can disperse throughout a building, it also may be necessary to inspect adjoining rooms and apartments.
A thorough inspection requires dismantling the bed and standing the components on edge so that upper and lower surfaces can be examined. Things to look for are the bugs themselves, and the light-brown, molted skins of the nymphs. Dark spots of dried bed bug excrement are often present along mattress seams or wherever the bugs have resided. Box springs afford many places for bed bugs to hide, especially underneath where the fabric is stapled to the wooden frame. Oftentimes the underlying dust cover must be removed to gain access for inspection and possible treatment. Successful treatment of mattresses and box springs is difficult, however, and infested components may need to be discarded. Cracks and crevices of bed frames should be examined, especially if the frame is wood. (Bed bugs have an affinity for wood and fabric more so than metal or plastic). Headboards secured to walls should also be removed and inspected. In hotels and motels, the area behind the headboard is often the first place that the bugs become established. Bed bugs also hide among items stored under beds.
Many areas besides beds, however, can harbor bed bugs.
Nightstands and dressers should be emptied and examined inside and out, then tipped over to inspect the woodwork underneath. Oftentimes, the bugs will be hiding in cracks, corners, and recesses.
Other common places to find bed bugs include: along and under the edge of wall-to-wall carpeting (especially behind beds and furniture); cracks in wood molding; ceiling-wall junctures; behind wall-mounts, picture frames, switch plates and outlets; under loose wallpaper; amongst clothing stored in closets; and inside clocks, phones, televisions and smoke detectors.
The challenge is to find and treat all places where bugs and eggs may be present. Bed bugs tend to congregate in certain areas, but it is common to find an individual or some eggs scattered here and there. Persistence and a bright flashlight are requisites for success. Inspectors sometimes also inject a pyrethrum-based, "flushing agent" into crevices to help reveal where bugs may be hiding. A thorough treatment of a home, hotel, or apartment may take up to several hours.
Bed bugs were treated years ago by wholesale spraying of beds, floors, walls, furniture, etc. with DDT. This practice is no longer permitted. Thoroughness is still very important, but treatments today are generally more targeted and judicious.
As mentioned earlier, owners and occupants have important pre-treatment responsibilities. Reducing clutter is a necessity. Belongings strewn about rooms afford many places for bed bugs to hide, and impedes inspection and treatment. Infested bedding and garments will need to be bagged and laundered (120F minimum), or discarded since these items cannot be treated with insecticides. Items that cannot be laundered can sometimes be de-infested by heating for several minutes in a clothes dryer. Other items can be wrapped in plastic and placed in a hot, sunny location for at least a few days (the 120F minimum target temperature should be monitored in the centermost location with a thermometer). Bedbugs also succumb to cold temperatures below 32 F, but the chilling period must be maintained for at least two weeks. Attempts to rid an entire home or apartment of bed bugs by raising or lowering the thermostat will be entirely unsuccessful. Most housecleaning measures are of little benefit in bed bug management. Site-specific vacuuming, however, can help remove some of the bugs before treatment with insecticides. Bed bugs (especially the eggs) can be difficult to dislodge. Optimum results will be achieved by moving and scraping the end of the suction wand along infested areas such as seams, tufts and edges of bedding, and the perimeter edge of wall-to-wall carpets. Afterward, dispose of the vacuum contents in a sealed trash bag. Steam cleaning of carpets may be helpful for killing bugs and eggs that vacuuming may have missed.
While the former measures are helpful, insecticides are important for bed bug elimination. Pest control professionals treat using a variety of low-odor sprays, dusts, and aerosols. (Baits designed to control ants and cockroaches are ineffective). Application entails treating all areas where the bugs are discovered, or tend to crawl or hide. Some bed bug species are parasites of bats or birds, and may bite people if the wild hosts are no longer available. If bat bugs or bird bugs are involved, roosting and nesting sites should also be treated and the animals excluded from the building.
Eliminating bed bugs from beds can be a challenge. If there are holes or tears in the fabric, the bugs and eggs may be inside, as well as outside. There also are restrictions on how beds can be treated with insecticides. For these reasons, pest control firms often recommend that beds be discarded, especially when heavily infested or in poor condition. Whether the bed stays or goes, encasing both the mattress and box spring is helpful if bugs are still present. Zippered encasements -- available at bedding and allergy supply stores -- deny bed bugs access to inner, hidden areas and entrap any bugs already inside. Some pest control firms treat seams, tufts, and crevices of bed components, but they will not spray the entire mattress surface, bed sheets, blankets, or clothing. Vacuuming (discussed previously) may further help to remove bugs and eggs from mattresses and box springs that cannot be discarded. Some pest control firms also treat beds with portable steam machines. The technique can be useful, but affords no residual protection and does not kill bugs or eggs hidden inside the box spring or mattress. Fumigation is another way to de-infest beds and hard-to-treat items, but the procedure is not always available. In extreme cases, entire buildings have been fumigated for bed bugs. The procedure is costly though, and involves covering the building in a tarp and injecting a lethal gas.
Concerned travelers may want to check their bed for telltale signs of the bugs -- a common practice years ago. This would entail examining the bed sheets and upper and lower seams of the mattress. Some professionals also suggest removal and examination behind the headboard, a frequent hiding place for the bugs in hotel rooms. If bed bugs are detected, travelers can request another room. Concerned travelers may also want to elevate suitcases off the floor (e.g. on a luggage stand). Inspecting or vacuuming luggage upon arriving home is less useful since it is hard to detect bed bugs inside a suitcase.
Although incidence of bed bugs in the United States is increasing, they remain rare in comparison to most other household pests. Familiarity can help to avoid infestation, or at least prompt earlier intervention by a professional.
CAUTION! Pesticide recommendations in this publication are registered for use in Kentucky, USA ONLY! The use of some products may not be legal in your state or country. Please check with your local county agent or regulatory official before using any pesticide mentioned in this publication.
Of course, ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW LABEL DIRECTIONS FOR SAFE USE OF ANY PESTICIDE!
This page was updated on April 26, 2014
More:
Bed Bugs - Colorado State University Extension

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location